AppleMagicTrackpad
|
Size: 6034
Comment: updated PPA instructions
|
Size: 5891
Comment: "gevdev" is now considered obsolete, and "synaptics" has the required functionality for proper MT on this device
|
| Deletions are marked like this. | Additions are marked like this. |
| Line 29: | Line 29: |
| Driver "evdev" | Driver "synaptics" |
| Line 44: | Line 44: |
| Driver "gevdev" | Driver "synaptics" |
| Line 58: | Line 58: |
| }}} Also note the driver is moving to evdev, so you may need to change the following line: {{{ Driver "evdev" }}} to: {{{ Driver "gevdev" |
The Magic Trackpad is a multi-touch trackpad produced by Apple Inc.
It can be used as a single-touch device in Ubuntu by pairing it using the Bluetooth utilities in Ubuntu. The following setup instructions only need to be followed once, then Ubuntu will recognize the Magic Trackpad without further configuration.
Also note the right and left buttons on the trackpad aas mouse buttons and are located under the device - the two rubber pieces act as such when you press *on* the device itself.
Note: This has been tested in Ubuntu Maverick (10.10) only.
Multitouch status
Support for the Magic Trackpad is not in Maverick yet. You need to add a PPA to your Ubuntu sources list in order to apt-get install it:
$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:utouch-team/utouch $ sudo apt-get update $ sudo apt-get install magicmouse-kernel-source
Xorg Setup
You need to pair the Magic Trackpad (see below, Pairing the Magic Trackpad) and, for the moment only, add this section to /etc/X11/xorg.conf:
Section "InputClass"
Identifier "multitouch touchpad"
MatchIsTouchpad "on"
# MatchDevicePath "/dev/input/event*"
Driver "synaptics"
EndSectionHere is an example of a complete xorg.conf file:
Section "Screen"
Identifier "Default Screen"
DefaultDepth 24
EndSection
Section "InputClass"
Identifier "multitouch touchpad"
MatchIsTouchpad "on"
# MatchDevicePath "/dev/input/event*"
Driver "synaptics"
EndSection
Section "Module"
Load "glx"
EndSection
Section "Device"
Identifier "Default Device"
EndSection
Section "ServerFlags"
Option "IgnoreABI" "True"
EndSectionAn very basic xorg.conf file can be generated to match your configuration by booting in recovery mode and executing:
# X -configure
Once Magic Trackpad support has landed, you hopefully won't need to edit your xorg.conf anymore.
Testing
You can confirm that gestures are cognized by following the directions here:
In order to use this device with other multi-touch software, you will need to know its input device name and number.
Here is example output for lsinput with a Magic Trackpad present (other irrelevant input device removed):
$ sudo lsinput /dev/input/event7 bustype : BUS_BLUETOOTH vendor : 0x5ac product : 0x30e version : 352 name : "Apple Wireless Trackpad" phys : "XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX" uniq : "XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX" bits ev : EV_SYN EV_KEY EV_REL EV_MSC
In this case the input device would be /dev/input/event7. The input device number would be 7.
For more information on testing this device for multi-touch support, see Multitouch/Testing.
Once you've confirmed the above, you can try using PyMT.
Pairing the Magic Trackpad
Using graphical tools
Once you have inserted batteries in your Magic Trackpad, if your system is Bluetooth-capable and its radio is enabled, you will see a dialog box asking for a PIN number to pair it:

Such pairing can be forced by pressing and holding the button at the top-right side of the tablet.
You need to provide 0000 as the PIN code and press Enter to pair the trackpad. Once this has been done you need to permanently authorize this device to pair with your system. You can do so by going to the Bluetooth applet and choosing Apple Wireless Trackpad > Connect:

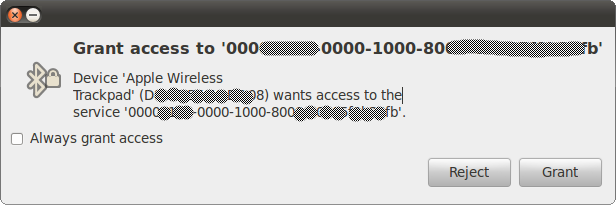
You will then be asked to confirm authorization to connect from this device. Make sure the "Always grant access" checkbox is ticked and click on Grant:
Once these steps have been completed the trackpad will remain available in Ubuntu.
If the above instructions fail, see below for manual Bluetooth pairing instructions.
Using the command line
First, verify that your Bluetooth radio is indeed on. Open a terminal window and issue the following command:
$ hcitool dev
Devices:
hci0 XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XXThe above example output shows what you would see if / when your Bluetooth radio is detected and enabled.
Next, let's scan for nearby Bluetooth devices. Note you must press the pairing/ON/OFF button for approximately 10 seconds on your Magic Trackpad for it to enter "pairing" mode. A small green light will start flashing.
$ hcitool scan
Scanning ...
XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX Apple Wireless TrackpadThe above output has important information. The bluez-compat package needs to be installed before requesting pairing:
$ sudo apt-get install bluez-compat
Then we can use the "XX..." string to request pairing of the trackpad:
$ sudo hidd --connect XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX
There should be no output after the above command, however your trackpad should now be recognized and act as a single-touch device.
Known issues
Related links
Multitouch - Ubuntu community documentation
Apple Magic Trackpad - Wikipedia entry
Apple Magic Trackpad - Apple product page
Apple Magic Trackpad and Ubuntu Lucid - How to pair the Magic Trackpad in Ubuntu 10.04 LTS
Multitouch/AppleMagicTrackpad (last edited 2013-10-21 16:13:22 by host86-136-125-87)
